Why Graphene will end semiconductors uses in electronics
Why Graphene will end semiconductors uses in electronics
There are compelling reasons for the industry’s fervent love affair with silicon: it’s cheap, plentiful, and a fantastic semiconductor. But if components are to keep up with the rate of change, it’s worth reexamining their foundation.
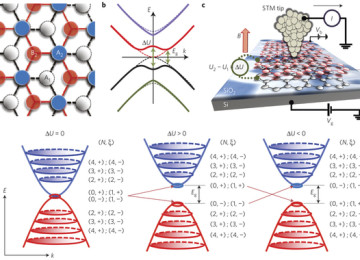
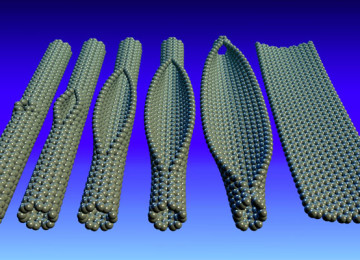
One promising contender is graphene, a sheet of carbon atoms that is only one atom thick. It’s much more energy efficient than silicon and dissipates heat faster as well. There’s evidence that graphene works even better when it’s combined with other polymers, too, making its potential applications innumerable. In the past, however, graphene hadn’t been able to be fabricated into narrow strips, and that prevented it from being incorporated into high-performance electronics.
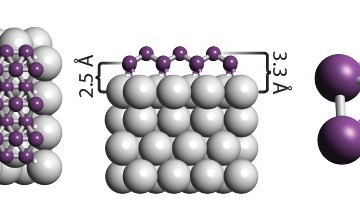
However, researchers at the University of Wisconsin have just figured out a way to grow graphene nanoribbons on germanium semiconductor wafers. This means that graphene nanoribbons are now able to be mass produced, making them useful in industrial and military applications, but could also be used for more pedestrian components like computer chips. It could also mean that they will allow designers to produce truly peculiar technology that isn’t possible with silicon.
This all comes down to graphene’s ability to boost the performance of the next generation of electronic devices, as they’re much more compatible with planar processing and much more efficient. Now that researchers have nailed the precision aspect of producing nanostrips, graphene is a strong contender for becoming silicon’s replacement and overhauling the semiconductor industry while rewriting the trajectory of the future.